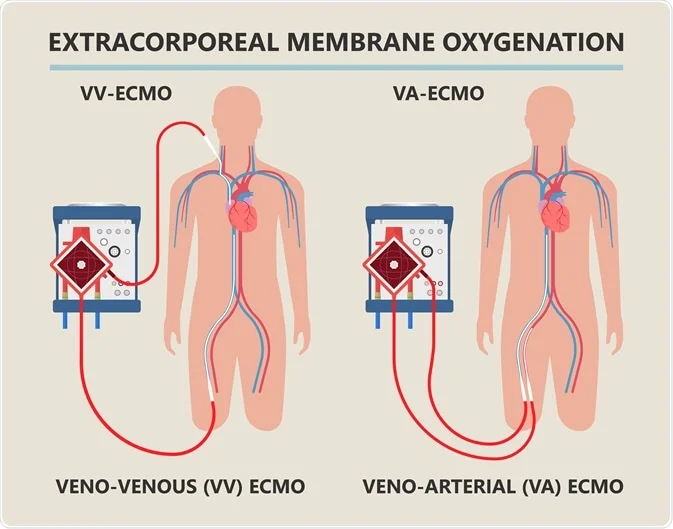
Maternal-Fetal Results of COVID-19-Infected Pregnant Women Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Descriptive Report
Objective: COVID-19 infection may produce severe pneumonia, mainly in the adult population. Pregnant women with severe pneumonia are at high risk of developing complications, and conventional therapy sometimes fails to reverse hypoxemia. Therefore, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is an option in cases with refractory hypoxemic respiratory failure. This study aims to evaluate the maternal-fetal risk factors, clinical characteristics, complications, and outcomes of 11 pregnant or peripartum patients with COVID-19 treated with ECMO. Study design: This is a retrospective descriptive study of 11 pregnant women undergoing ECMO therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Results: In our cohort, four patients underwent ECMO during pregnancy (36.3%) and 7 during the postpartum period. Initially, they started on venovenous ECMO, and three patients were required to change modality due to clinical conditions. In total, 4/11 pregnant women (36.3%) died. We established two periods that differed in the implementation of a standardized care model for reducing associated morbidities and mortality. Neurological complications were responsible for most deaths. Regarding fetal outcomes at early-stage pregnancies on ECMO (4), we report three stillbirths (75%), and one newborn (twin pregnancy) survived and had a favorable evolution. Conclusion: At later-stage pregnancies, all newborns survived, and we did not identify any vertical infection. ECMO therapy is an alternative for pregnant women with severe hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19, and may improve maternal and neonatal results. Regarding fetal outcomes, the gestational age played a definitive role. However, the main complications reported in our series and others are neurological. It is essential to develop novel, future interventions to prevent these complications. Thieme. All rights reserved. PubMed Disclaimer